Marginal Revenue Calculator
Calculate additional revenue from selling one more unit of product.
What is Marginal Revenue?
Marginal revenue (MR) is the additional revenue generated from selling one more unit of a product or service.
Marginal revenue is the extra money a company makes by selling one more unit. It’s calculated by dividing the change in total revenue by the change in quantity sold.
It’s crucial for businesses as it helps determine production levels, pricing, and profit maximization. It also indicates market power and competition levels.
In perfect competition, marginal revenue equals the product’s price. In less competitive markets, it usually decreases as more units are sold, often due to price reductions to increase sales.
Marginal Revenue Formula
Marginal Revenue Calculation Examples
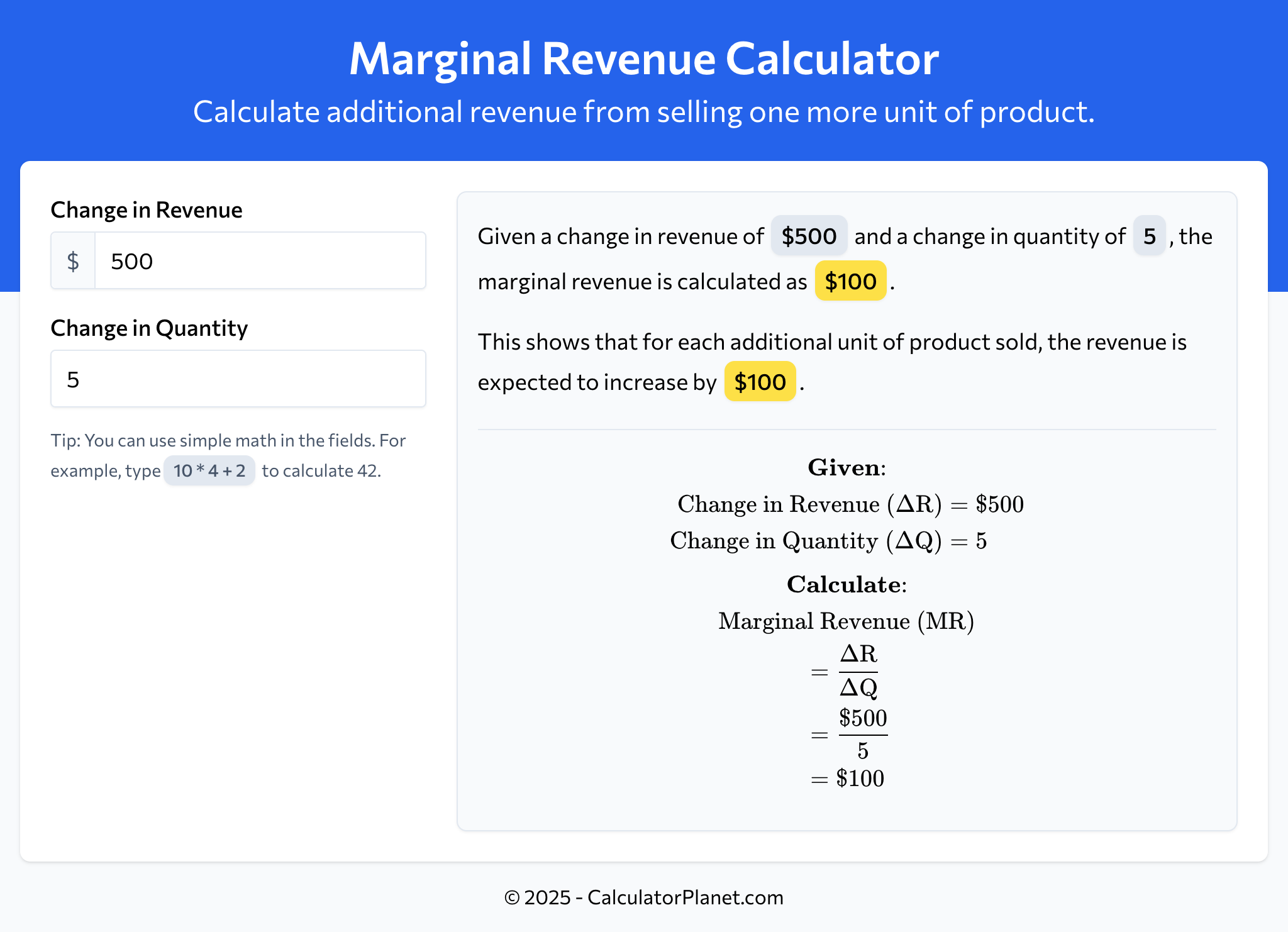
Example 1
A software company introduces a new feature in their product. They observe that by selling 5 additional licenses, their revenue increases by $500.
Let's calculate the marginal revenue:
This indicates that each additional license sold contributes $100 to the company's revenue.
This information can help the company decide on pricing strategies and whether to invest in marketing to promote this new feature.
Example 2
A farmer decides to expand their organic vegetable production. They find that by increasing their harvest by 100 bushels, they can increase their revenue by $2,000.
Let's calculate the marginal revenue for this expansion:
This result shows each additional bushel of organic vegetables adds $20 to the farmer's revenue.
The farmer can use this to assess if expanding production costs are justified by the marginal revenue.
Reference This Page
If you found our Marginal Revenue Calculator valuable, please consider referencing this page in your work. You can easily cite it by using the following formatted text:
More Calculators
- Annualized Return Calculator
- Break-Even Point Calculator
- Buying Power Calculator
- Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) Calculator
- Cost of Goods Sold Calculator
- Current Ratio Calculator
- Debt to Equity Ratio Calculator
- Dividend Yield Calculator
- Earnings Per Share (EPS) Calculator
- Free Cash Flow (FCF) Calculator
- Future Value Calculator
- Gross Margin Calculator
- Marginal Revenue Calculator
- Markup Calculator
- Net Present Value (NPV) Calculator
- Operating Leverage Calculator
- Operating Margin Calculator
- Payback Period Calculator
- Present Value Calculator
- Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E) Calculator
- Profit Margin Calculator
- Return on Assets (ROA) Calculator
- Return on Equity (ROE) Calculator
- Return on Investment (ROI) Calculator
- Revenue Growth Calculator
- Total Revenue Calculator
- Variable Cost Ratio Calculator
- Working Capital Calculator